The legitimacy of digital artwork is notoriously difficult to establish. This is where NFTs, also known as non-fungible tokens, come into play. These tokens create a chain of ownership that can be viewed by the public but cannot be altered. Find out more about the process of creating NFT art and the steps that need to be taken in order for you to make your own.
NFTs, also known as non-fungible tokens, have taken over the art world in much the same way that Bitcoin has taken over the financial markets. They are a lucrative new toy that is met with enthusiasm by some people and skepticism by others.
It is possible for individual works of NFT art to sell for thousands or millions of pounds. They have even been purchased at Christie’s, which is widely regarded as the preeminent art auction house in the world.
However, given that NFTs primarily represent digital assets, it might be challenging to wrap one’s brain around the concept of what it means to truly own an NFT artwork.
The subject of what NFT art is and how one might produce their own is addressed in the following section of this article.
The Meaning Of NFT Art
In the past, every single duplicate of a digital artwork had the same potential worth – or lack of value, depending on your perspective. In theory, the NFTs have made this different.
Art created with NFT can take the form of a movie, an image, a song, or even something completely else. When it comes to NFTs, the non-fungible packaging of the artwork is more important than the artwork itself.
When you purchase a piece of NFT art, you are also purchasing a certificate attesting to the artwork’s authenticity and stating that you are the rightful owner of the item.
This certificate will include an identification code and metadata that will contain a series of specified elements that indicate its one-of-a-kind status and record of ownership. These elements can be found in the certificate. It is for this reason that non-fungible tokens cannot be exchanged for other tokens.
A non-fungible token (NFT) can at most ever have a single owner at any given moment, and the proof of this fact is incorporated into the non-fungible token itself and can be easily and publicly verified.
After then, a transparent record of ownership will be made, which will thereafter be expanded each time the NFT artwork is sold on in the years to come. Because of this, it is possible to easily track the history of the work of art that has been minted as an NFT, and as a result, determine its legitimacy.
When seen from the point of view of the creator, on the other hand, it enables them to attach a price tag and a chain of ownership to a piece of digital artwork that, in the past, had no tangible worth and could be freely circulated. Even if the artwork in question continues to be publicly accessible online.

What Is NFT Art Good For?
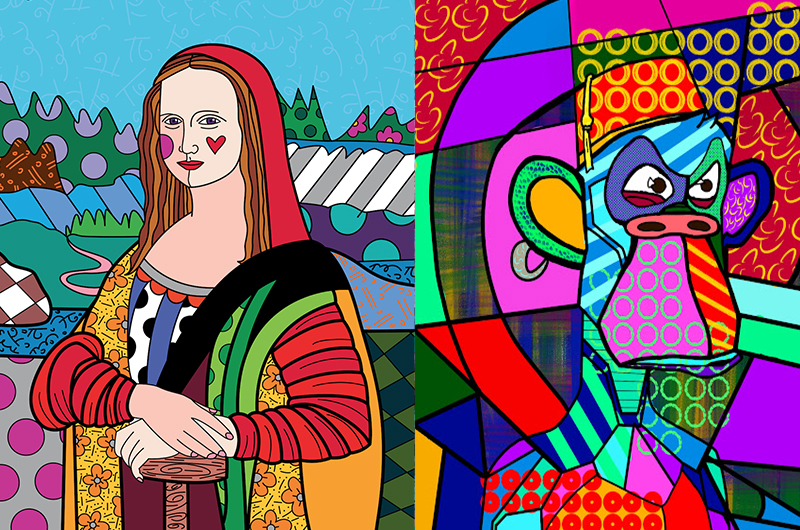
Let’s imagine that someone “minted,” or made, an NFT of a picture of the Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci. This would mean that they created the image. You would not be the owner of the Mona Lisa if you purchased that NFT. If it were still there, it would be displayed in the Louvre.
You also would not own the picture file of the painting, which means that you would not have the ability to prevent it from being displayed elsewhere, as you would if it were a tangible piece of art.
Additionally, you would not have ownership of the copyright. Although some non-fungible tokens (NFTs) may come with the copyright to the original artwork, this right is not necessarily transferred to the purchaser of all non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
This indicates that you would not be granted permission to replicate and sell anything that was included within the NFT. You were only able to sell the NFT on its own. In a normal situation, the same would be true of physical art.
In the case of the Mona Lisa, you would have the certificate attesting to its authenticity as well as proving that you are the rightful owner of this particular digital reproduction of the painting. And due to the operation of NFTs, there is no other party that might call into question that record of ownership.
After that, you would be able to sell this NFT at a later time, maybe at a price that is more (or lower) than what you paid for it initially.
NFT Artworks
The example of a Mona Lisa NFT that was provided earlier may have led some people astray due to the fact that the Mona Lisa was not initially a digital artwork. It is an actual painting, and there is only one copy in existence. There are a variety of methods available to verify its legitimacy.
The majority of works of art produced by NFT will initially exist only in digital form. That is to say, they are not digital representations of anything tangible; rather, they are digital on their own. Because of this, it is normally extremely difficult, if not impossible, to demonstrate that you are in possession of the “original” piece of artwork because each replica is virtually indistinguishable from the other. NFTs make an effort to find a solution to this challenge.
The ideas of what constitutes an artwork have been called into question as a result of NFT art. Memes like “Disaster Girl” and “Success Kid” as well as viral media like “Charlie Bit My Finger” have fetched prices in the thousands of dollars.
The ideas of what constitutes an artwork have been called into question as a result of NFT art. Memes like “Disaster Girl” and “Success Kid” as well as viral media like “Charlie Bit My Finger” have fetched prices in the thousands of dollars.

How To Create A NFT
It is not too difficult to make your own works of NFT art, if that is something you are interested in doing.
To begin, you would have to actually make the piece of art itself. It doesn’t matter what this is, as long as it can be converted into a digital file.
If you wanted to mint an NFT of an artwork that wasn’t created by you, the first thing you would need to do is get permission from the person who owns the copyright to the artwork.
In addition to this, you would need to make sure that you had ether stored in a cryptocurrency wallet (ETH). Both the funding and storage of the newly minted NFTs will be handled in this manner.
The next step is to decide where you would like to mint your NFT, so get ready for that. You can create new NFTs on many of the same marketplaces where you can buy existing ones. This is known as “minting.”
Although every site will have its unique method of minting, in general, you will be asked to do the following:
Upload the file that corresponds to the newly created digital asset.
Include a heading along with a description in your NFT.
Determine the price at which your NFT will be sold, often known as the opening bid price.
There is a possibility that you will be required to pay gas fees in order to mint an NFT, and these fees vary depending on the platform that you use.
The Ethereum miners, who supply the computing power for the entire NFT process, are the recipients of a gas charge that is paid directly to them. This fee is dynamic and is determined by the level of activity on the Ethereum network at the moment the coin is being mined.
Following the completion of these processes, you will be able to start selling your very own NFT. It is even possible that in the future you will be eligible to collect royalties whenever the NFT is sold.